The Automation Revolution: Your Guide to the Software Stack of 2025
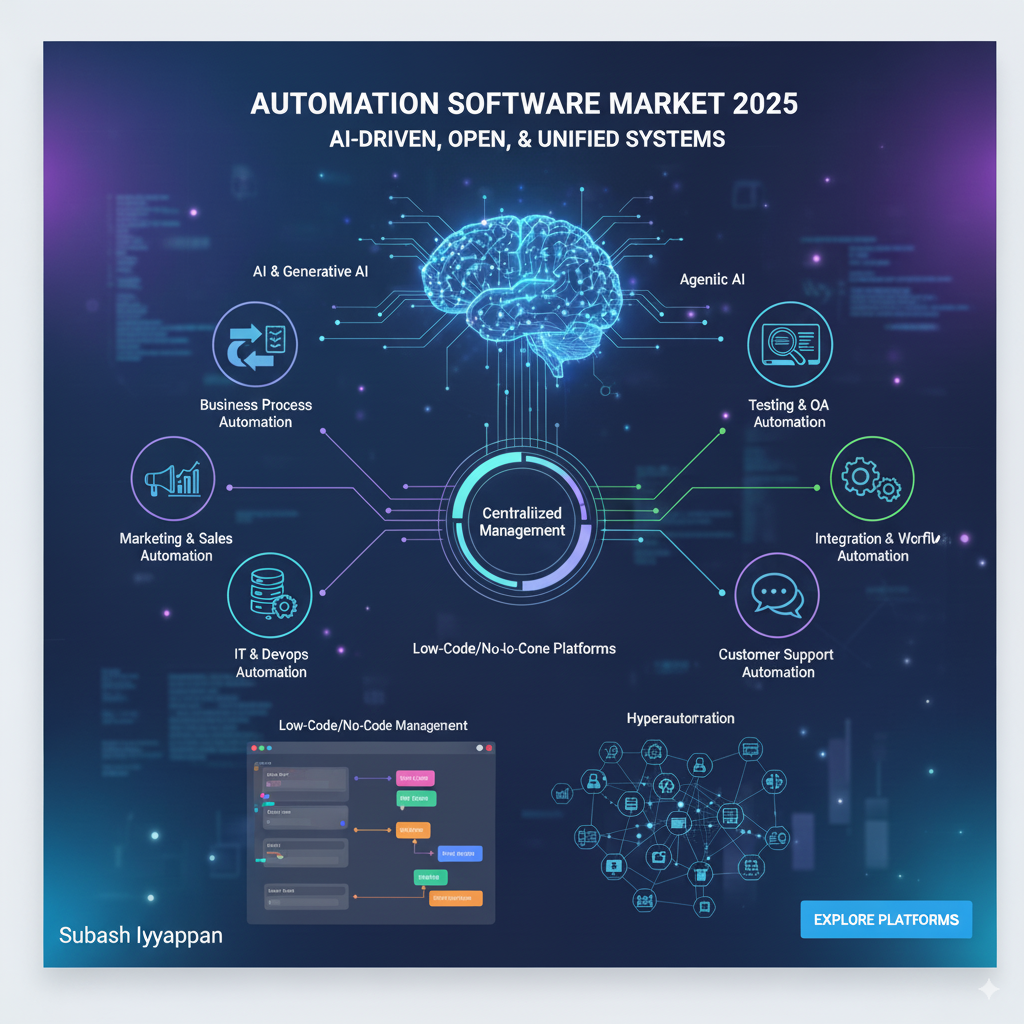
As of 2025, the market for automation software is evolving at a rapid rate, driven by increasing infusions of artificial intelligence (AI) and demands for more open, easier-to-use systems. Software in use cases can be broadly categorized by the business function it addresses, with some platforms being versatile enough to span departments.
Major Trends in Automation Software:
Several major trends are shaping the market for automation software in 2025:AI and Generative AI Integration: This is arguably the most critical trend. Automation tools are moving beyond simple, rule-based workflows to adopt AI for more intelligent, autonomous, and adaptive tasks. These include AI-powered chatbots, automated document processing, and predictive analytics for uncovering new automation opportunities.
Agentic AI: These are AI agents that possess the ability to act autonomously to achieve a goal without being intervened by humans constantly. In the year 2025, agentic AI is gaining traction, with software that can monitor systems, detect fraud, and even rectify it on their own.
Hyperautomation: This is the trend for combining multiple technologies—such as Robotic Process Automation (RPA), AI, machine learning (ML), and process mining—to automate complex, end-to-end business processes.
Low-Code/No-Code Platforms: Automation is being exposed to non-technical users, also referred to as “citizen developers.” These platforms are using visual, drag-and-drop interfaces to allow business users to develop their own workflows, fostering automation democracy and reducing the reliance on IT organizations.
Centralized Management: Organizations are evolving from disparate, siloed automation “islands” to a single, centralized platform that can manage and orchestrate automation across various departments and applications.
Typical Use Cases and Corresponding Software.
Below is a list of typical use cases and categories of software in use in 2025:
1. Business Process Automation (BPA)
Such solutions are put in place to automate and organize internal processes, approvals, reporting, and task management.
Software Examples:
Kissflow: No-code platform to create business applications to automate processes.
Pipefy: Transforms scattered approval processes into structured, automated workflows.
Microsoft Power Automate: A cloud application that enables businesses to automate workflows and integrate applications.
2. Marketing and Sales Automation:
Software that helps teams automate repetitive tasks like lead nurturing, email campaigns, and CRM management.
Software Examples:
HubSpot: An all-in-one solution that combines CRM with marketing and sales automation functionality.
ActiveCampaign: Focuses on email marketing and CRM with advanced automation workflows.
Salesforce: A leading CRM with advanced automation capabilities for sales workflows.
3. IT and DevOps Automation
These tools are necessary for automating technical environments, including infrastructure, deployments, and monitoring.
Software Examples:
Jenkins: An open-source automation server for continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipelines.
Ansible: Automates software provisioning, configuration management, and application deployment.
Terraform: An infrastructure-as-code tool for building, changing, and versioning infrastructure safely and efficiently.
UiPath: An enterprise RPA platform that uses AI agents and bots to automate complex business processes.
4. Customer Support Automation
This software helps support teams manage incoming requests, cut response times, and improve the customer experience.
Software Examples:
Zendesk: Customer service software with ticket routing and chatbot responses.
Intercom: Offers conversational support with automated chat and post-resolution surveys.
Freshdesk: Help desk software that automates customer communication and ticket management.
5. Integration and Workflow Automation
These platforms act like the glue between applications, allowing them to communicate with one another and trigger actions.
Software Examples:
Zapier: One of the most popular tools among small businesses, connecting over 8,000 apps to automate workflows without coding.
Make (formerly Integromat): A powerful visual platform for building multi-step, real-time automation between different services.
6. Testing and Quality Assurance (QA) Automation:
In 2025, test automation has become a vital component of the software development life cycle.
Software Examples:
Selenium: A classic open-source web browser test automation tool.
Playwright: Microsoft’s open-source end-to-end web application testing framework.
Katalon Studio: Low-code test automation suite for testing web, mobile, and APIs.
Leapwork: No-code, visual test automation platform that empowers enterprises to test software easily.

 Bitcoin
Bitcoin  Ethereum
Ethereum  Tether
Tether  XRP
XRP  USDC
USDC  Solana
Solana  TRON
TRON  Lido Staked Ether
Lido Staked Ether  Figure Heloc
Figure Heloc  Dogecoin
Dogecoin  WhiteBIT Coin
WhiteBIT Coin  USDS
USDS  Cardano
Cardano  Bitcoin Cash
Bitcoin Cash  Wrapped stETH
Wrapped stETH  LEO Token
LEO Token  Hyperliquid
Hyperliquid  Wrapped Bitcoin
Wrapped Bitcoin  Monero
Monero  Binance Bridged USDT (BNB Smart Chain)
Binance Bridged USDT (BNB Smart Chain)  Chainlink
Chainlink  Ethena USDe
Ethena USDe  Canton
Canton  Stellar
Stellar  Wrapped eETH
Wrapped eETH  USD1
USD1  Dai
Dai  sUSDS
sUSDS  Rain
Rain  PayPal USD
PayPal USD  Litecoin
Litecoin  Coinbase Wrapped BTC
Coinbase Wrapped BTC  Hedera
Hedera  Avalanche
Avalanche  Sui
Sui  WETH
WETH  Zcash
Zcash  Toncoin
Toncoin  Shiba Inu
Shiba Inu  USDT0
USDT0  Cronos
Cronos  Tether Gold
Tether Gold  World Liberty Financial
World Liberty Financial  MemeCore
MemeCore  PAX Gold
PAX Gold  Polkadot
Polkadot  Uniswap
Uniswap  Ethena Staked USDe
Ethena Staked USDe